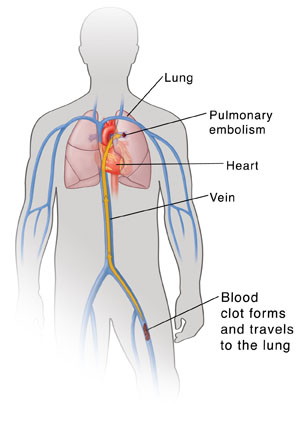
A pulmonary embolus is most often due to a blood clot that develops in a deep vein of the leg (deep vein thrombosis). If that clot breaks loose and travels to the lung, it's called a pulmonary embolism (PE). This can cut off blood flow in the lungs.
A blood clot in the lungs is a medical emergency and may cause death.
Healthcare providers use the term venous thromboembolism (VTE) to describe these 2 conditions: deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. They use the term VTE because the 2 conditions are very closely linked. And because their prevention and treatment are also closely linked.
How is pulmonary embolism diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider examines you and asks about your symptoms and health history. You may also have one or more of the following:
-
Blood tests to check for blood clotting or other problems
-
Imaging tests to look for clots in the veins or lung
-
Electrocardiography (ECG) to test how well the heart is working
How is pulmonary embolism treated?
-
Blood-thinning medicines (anticoagulants). These medicines thin the blood. They may be given as a pill, as an injection, or through a tube into a vein (intravenous or IV). Blood thinners help prevent more blood clots from forming. They also help to prevent an existing clot from getting larger.
-
Thrombolysis. Thrombolytic medicines are used to quickly dissolve a blood clot. A long, narrow tube (catheter) is used to deliver medicine directly to the clot. Thrombolytic medicines increase the risk of bleeding. So they are used very carefully.
-
Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter surgery. The vena cava is the body’s largest vein. It carries blood from the body to the heart. A small filter traps blood clots in the lower body and prevents them from traveling to the lungs. The filter is inserted into the vein through a catheter. The filter may be used if blood thinners can't be taken or if they don't work.
-
Pulmonary embolectomy. This is a procedure to remove a blood clot in the lungs. It may be done with surgery or with a catheter inserted in the body. It may be done when other treatments aren't safe or don't work.
What are the long-term concerns?
With treatment, blood clots are often dissolved or removed. Some treatments can even help prevent future clots. But having a PE can put you at risk for another life-threatening blood clot. So, you will likely need to take anticoagulants to help keep blood clots from forming again. You may need to take this medicine for months or years.
You may also need to make lifestyle changes. This may include getting more active and eating healthier. You may need to wear elastic (compression) stockings and take breaks on long trips.
Call 911
Call
-
Heavy or uncontrolled bleeding
-
Symptoms of a blood clot that has traveled to the lungs, including:
-
Chest pain
-
Trouble breathing
-
Coughing (may cough up blood)
-
Fainting
-
Fast heartbeat
-
Sweating
-
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider if you have swelling or pain in your leg, arm, or other area. These are symptoms of a blood clot.
You may have bleeding if you take medicine to help prevent blood clots.
Call your provider if you have symptoms of bleeding. This includes:
-
Blood in your pee
-
Bleeding with your poop (stool or bowel movements)
-
Bleeding from the nose, gums, vagina, or a cut