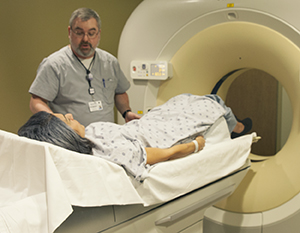
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging test. It's done with X-rays and a computer. First, a series of X-rays are taken from different angles around your body. Then the images are processed by a computer. The computer makes them into cross-section images called slices. The result is a detailed set of images. They can show problems with soft tissues, organs, blood vessels, and bones.
Tell the technologist
The technologist is the person who does your scan. Make sure to tell them if you:
-
Ever had a reaction to contrast dye
-
Have kidney problems
-
Take diabetes medicine
-
Are pregnant or think you may be
-
Ate or drank anything before the test
Before your test
-
Follow any directions you’re given for not eating or drinking before the test.
-
You may have to drink contrast material before the test. This depends on the type of test you will have. Your provider or the facility will give it to you if needed.
-
Arrive on time for the scan.
-
When you arrive, you may be asked to change into a hospital gown. Remove all metal near the part of your body that will be scanned. This includes jewelry, glasses, and dentures. You may need to remove your bra if it has a metal underwire.
Tell the healthcare team:
-
If you are pregnant or think you may be
-
If you have ever had a reaction to contrast dye. You may need to take medicine before your scan.
-
If you have a history of kidney disease. You may not be able to have IV (intravenous) contrast dye if your kidneys aren't working well.
-
All the medicines you take. This includes prescription and over-the-counter medicines. It also includes vitamins, herbs, and other supplements. Ask if it's OK to take them before the test.
During your test
-
You may be given contrast material through an IV line, enema, or by mouth. If you have it through an IV, you may feel warm or flushed. You may have a metallic taste in your mouth. Or you may feel the need to pee. These are normal side effects. They should go away quickly.
-
Tell the technologist if you have chest pain, shortness of breath, swelling in the throat, or a feeling that your heart is racing (palpitations).
-
You will lie on a scanner table. The table slides into the CT scanner.
-
The technologist will operate the scanner from a control room. They will be able to hear you and speak to you.
-
The technologist will ask you to hold your breath for a few seconds during your scan.
After your test
-
You can go back to your normal diet and activities right away.
-
Any contrast dye will pass naturally through your body within 1 to 2 days.
-
Before leaving, you may need to wait while your images are being reviewed. Your healthcare provider will discuss the test results with you during a follow-up appointment or over the phone.