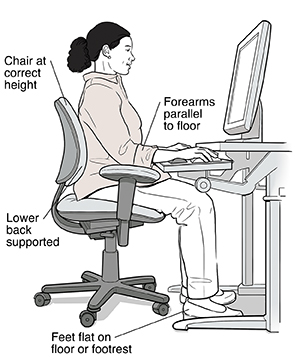
If you sit much of the day, your chair is your main support. A well-adjusted chair improves your circulation. It also helps prevent backaches and fatigue. You can increase your comfort by adjusting the chair's backrest position and height to fit your body.
Backrest
-
Sit at your workstation, leaning back slightly with your back firmly against the chair and the shoulders touching the backrest. The backrest should fit snugly against your lower back.
-
If it doesn't , adjust the backrest until your lower back is fully supported. Adjust the height of the backrest to support the natural inward curvature of the lower back.
-
If you can't adjust the backrest , use a small, thin, firm pillow or rolled-up towel or lumbar pad to support your lower back.
-
The backrest angle should be set so that your hip-torso angle is 90 ° or greater.
-
Use a chair with a backrest that is easily adjustable and able to support the back in a variety of seated postures.
Chair height
Arm position
-
Place your fingers on the keyboard's middle row of letters. Your upper arms should hang comfortably at your sides, and your shoulders should be relaxed while keyboarding. Your forearms should be parallel to the floor.
-
If they are not , adjust your chair height until your forearms are parallel to the floor.
-
When armrests are used, elbows and lower arms should rest lightly so as not to cause circulatory or nerve problems.
-
Position adjustable armrests so they support your lower arm and allow your upper arm to remain close to the torso. Don't use the armrests to slouch.
-
Armrests should be made of a soft material and have rounded edges.
Leg position
-
Keep your knees at or below the level of your hips. It may help to slide your feet forward until your knees are at a 90 to 110 degree angle. Your feet should rest firmly on the floor. There should be 1 to 2 inches of legroom between your lap and desk or keyboard tray.
-
If you have less than 2 inches of legroom, try to raise your desk or keyboard tray height.
-
If you can't adjust your chair height and your feet don't reach the floor, use something as a footrest. A box or binder can work. If you wear flat shoes, a level surface works best. If you wear heels, a slanted surface is better.
-
The back of your knees should not come in direct contact with the edge of the seat pan (there should be 2 to 3 inches between the edge of the seat and the back of the knee).
-
Your thighs should be parallel to the floor and your knees at about the same level as your hips.