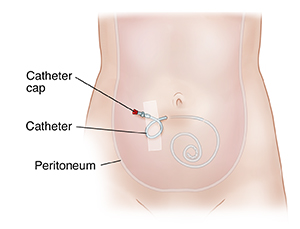
Your kidneys filter and remove waste from your blood. When they fail, this work must be done some other way. Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a treatment that can take over when your kidneys stop working. The peritoneum is the membrane lining the inside of your abdomen (belly). PD uses the lining of your abdomen as a filter for your blood. Before PD can be done, an opening into this lining (an access) must be made. The access for PD is a soft tube called a catheter placed into your abdomen.
Placing the catheter
-
A nurse or anesthesiologist gives you medicine so you don’t feel pain during surgery.
-
A small opening is made just below your belly button (navel). The catheter is placed through this opening.
-
One end of the catheter sits in your abdomen. A few inches of the other end comes out an exit site in your skin. This end is clamped off and capped when it’s not being used.
-
Typically, a part of the catheter goes through a tunnel made underneath the skin before it enters your abdomen. This tunnel helps prevent infections from entering your abdomen. It also holds the catheter in place to keep it from falling out.