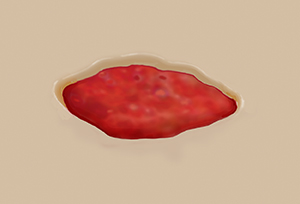
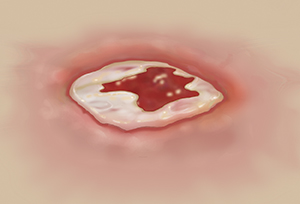
Wounds can become infected with harmful germs (bacteria). This prevents healing. It also increases your risk of scars. In some cases, the infection may spread to other parts of your body. An infection with the bacteria that causes tetanus can be fatal. Know what to look for and get prompt treatment for infection.
What are the risk factors for infection?
A wound is more likely to become infected if it:
-
Results from a hole (puncture), such as from a nail or piece of glass.
-
Results from a human or animal bite, especially a cat.
-
Isn't cleaned or treated soon after occurring.
-
Occurs in your hand, foot, leg, armpit, or groin (the area where your belly meets your thighs).
-
Contains dirt or saliva.
-
Heals very slowly.
-
Occurs and you have diabetes, alcoholism, a weak immune system, or poor blood circulation.
What are the symptoms of infection?
Call your health care provider at the first sign of infection, such as:
-
Redness or warmth around the wound.
-
Edges look like they are opening.
-
Yellow, yellow-green, white, or foul-smelling drainage from a wound.
-
More pain, swelling, or redness in or near a wound.
-
A change in the color or increase in the size of a wound.
-
Red streaks in the skin around the wound.
-
A fever.
How are infections treated?
Treatment depends on the type of infection you have, and how serious it is. Your health care provider may prescribe oral antibiotics to help fight bacteria. Your provider may also clean the wound with an antibiotic solution or apply an antibiotic ointment. Sometimes a pocket of pus (abscess) may form. In that case, the abscess will be opened and the fluid drained. You may need hospital care if the infection is very severe.
Preventing wound infection
Follow these steps to help keep wounds from getting infected:
-
Wash the wound right away with soap and water.
-
Consider applying a small amount of antibiotic ointment. You can buy this without a prescription.
-
Cover wounds with a bandage or gauze dressing. Change it daily or whenever it gets wet or dirty.
-
Keep the wound clean and dry for the first 24 hours.
-
Wash your hands before and after you care for your wound.
-
Change the dressing daily. Follow the instructions your health care provider gave you.