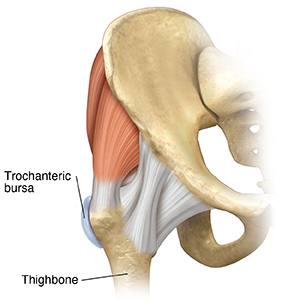
A bursa is a thin, slippery, sac-like film. It contains a small amount of fluid. It's found between bones and soft tissues in and around joints. A bursa cushions and protects a joint. It keeps parts of a joint from rubbing against each other. If a bursa becomes inflamed and irritated, it's known as bursitis.
The trochanteric bursa is found on the hip joint. It lies on top of the bump at the top of the thighbone called the greater trochanter. Inflammation of this bursa is called trochanteric bursitis.
How to say it
troh-kan-TAYR-ihk
Causes of trochanteric bursitis
Causes may include:
-
Overuse of the hip during running or other sports, dance, or work.
-
Falling on or irritating the side of the hip.
This condition may occur along with other problems, such as osteoarthritis of the hip or knee, or low back problems. In rare cases, it may occur after hip surgery.
Symptoms of trochanteric bursitis
Symptoms may include:
-
Pain or aching on the side of the hip. It's often felt as a sharp, intense pain. The pain may travel down the leg.
-
Swelling, tenderness, or warmth on the side of the hip at the bony bump at the top of the thigh.
Treatment for trochanteric bursitis
These may include:
-
Resting the hip. This allows the bursa to heal.
-
Prescription or over-the-counter pain medicines. These help reduce inflammation, swelling, and pain. NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are the most common medicines used. Medicines may be prescribed or bought over the counter. They may be given as pills. Or they may be put on the skin as a gel, cream, or patch.
-
Cold packs and heat packs. These help reduce pain and swelling.
-
Stretching and strengthening exercises. These improve flexibility and strength around the hip.
-
Physical therapy. This includes exercises or other treatments.
-
Injections of medicine into the bursa. This may help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. The medicine is usually a corticosteroid. This is a strong anti-inflammatory medicine.
Possible complications
If you don’t give your hip time to heal, the problem may not go away, may return, or may get worse. Rest and treat your hip as directed.
When to get medical advice
Contact your health care provider right away if you have:
-
A fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider.
-
Chills.
-
Redness, swelling, or warmth that gets worse.
-
Symptoms that don’t get better with prescribed medicines or that get worse.
-
New symptoms.
Author: Michels, Karen
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.