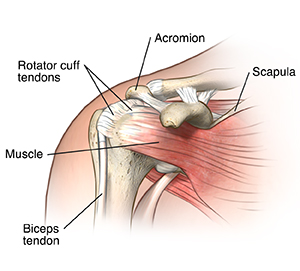
What is shoulder tendonitis?
Shoulder tendonitis is an inflammation of your rotator cuff or biceps tendon. Your rotator cuff consists of the muscles and tendons in your shoulder. They connect your upper arm bone to your shoulder blade.
Your injury may range from mild to severe inflammation of most of your rotator cuff. When your rotator cuff tendon gets inflamed and thickened, it is also called rotator cuff tendonitis. Your rotator cuff tendon may get trapped under the top bone of your shoulder (acromion). It is formed by a part of your shoulder blade (the scapula).
What causes shoulder tendonitis?
Shoulder tendonitis is often caused by a tendon being pinched by nearby structures. The condition often occurs in certain sports that need your arm to move over your head repeatedly. Such sports include baseball, weightlifting, volleyball, racket sports, and certain swimming strokes.
What are the symptoms of shoulder tendonitis?
Symptoms may be a bit different for each person. Symptoms may include:
-
Inability to hold your arm in certain positions
-
Shoulder pain, weakness, or soreness
-
Pain at night
-
Sudden pain with lifting and reaching movements
The symptoms of shoulder tendonitis may seem like other conditions or health problems. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is shoulder tendonitis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will take a full health history and do a physical exam. You may also need diagnostic tests, such as:
-
X-ray. Invisible electromagnetic energy beams produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Ultrasonography. High-frequency sound waves create an image of some part of the inside of your body.
-
MRI. Large magnets and a computer make detailed images of organs and structures in your body.
How is shoulder tendonitis treated?
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how bad the condition is.
Treatment may include:
-
Rest
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
-
Strengthening exercises
-
Physical therapy
-
Ultrasound therapy
-
Corticosteroid shot (injection)
-
Surgery (for severe injuries or tears)
What are possible complications of shoulder tendonitis?
If treatment is not started when your pain and discomfort are fairly mild, problems may develop. These may include:
-
Pain that interrupts your sleep
-
Loss of strength or motion in your affected arm
-
Pain when moving the shoulder
-
Trouble doing things that need moving your injured arm behind your back or overhead. This includes doing things such as fastening zippers or buttons. Or placing objects in high places.
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider if:
-
Your pain gets worse
-
It gets harder to move your injured arm
-
Your pain disrupts your sleep
-
Your pain and discomfort keep you from doing your normal activities
-
You have numbness or tingling into your arms or hands
Key points about shoulder tendonitis
-
Shoulder tendonitis is an inflammation of your rotator cuff or biceps tendon. It often results from your tendon being pinched by nearby structures.
-
You can get shoulder tendonitis from playing certain sports that need the arm to move over the head repeatedly.
-
Symptoms can include not being able to hold your arm in certain positions and pain or soreness in your shoulder.
-
Diagnosis can be made from a health history, physical exam, and tests, such as X-ray and MRI.
-
Treatment may include rest, medicines, strengthening exercises, ultrasound therapy, and corticosteroid shots.
-
Surgery is used for severe injuries or tears.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
-
Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
-
Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
-
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
-
At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
-
Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed and how it will help you. Also know what the side effects are and when they should be reported.
-
Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
-
Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
-
Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
-
If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
-
Know how you can contact your healthcare provider if you have questions, especially after office hours or on weekends and holidays.