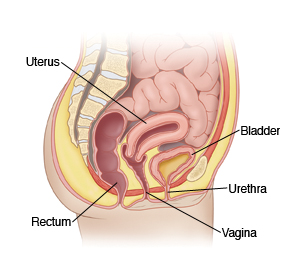
Any object placed inside the vagina is called a vaginal foreign body.
Small amounts of tissue paper are the most common vaginal foreign body found in young children. In some cases, young children curious about their bodies may place small objects inside the vagina. This can include things like crayons, beads, coins, batteries, or twigs. Rarely, these may be a sign of sexual abuse.
If an object is left inside the vagina or becomes stuck, it can cause symptoms over time. If not removed, it can also lead to infection and damage nearby tissues. A battery in the vagina can quickly cause a serious burn of the vagina.
Symptoms may include unusual or foul-smelling discharge from the vagina. Bleeding, redness, swelling, or rash may also occur. Some children may feel pain or pressure in or around the vagina. They may also have problems passing urine and stool. These symptoms should raise suspicion for a vaginal foreign body, because young children will not often report that they put an object into their vagina.
Treatment involves removing the object. Once the object is removed, symptoms should go away. If the object caused an infection, antibiotics may be given.
Home care
-
If medicine is prescribed, be sure to give it to your child as directed. Make sure your child finishes all of the medicine even if they start to feel better.
-
To help soothe irritation, have your child soak in a bath with a few inches of warm water a few times a day. Don’t add any bath products to the water. Also, don't wash the affected area with soap. Rinse the area and pat it dry instead.
-
To help prevent your child from having the problem again:
-
Explain in an age-appropriate manner why it's important not to put anything in the vagina.
-
Teach your child to wipe from front to back after using the bathroom.
-
Keep small objects out of reach and stored in a safe place. Be especially careful where you store batteries. These can leak and cause burns if placed inside the body.
-
Follow-up care
Follow up with your child’s healthcare provider, or as directed.
When to get medical advice
Unless your child’s healthcare provider advises otherwise, call the provider right away if any of the following occur:
-
Your child has a fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider.
-
Your child has vaginal discharge or slight bleeding.
-
Your child’s symptoms don’t improve or get worse.
-
Your child develops pain in the belly.
-
Your child has burning or pain during urination.
Call 911
Call
-
Your child feels weak, dizzy, or faint
-
Your child has a large amount of vaginal bleeding
Featured in