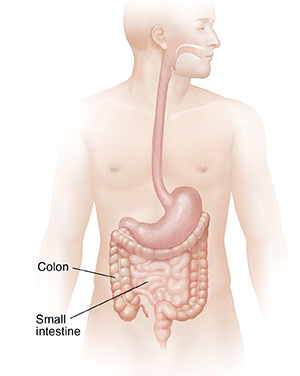
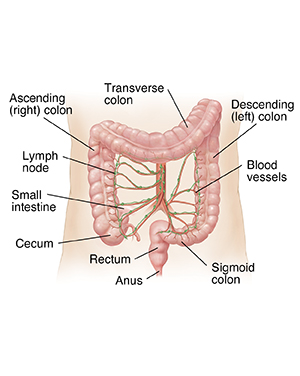
The colon (large intestine) is a muscular tube that forms the last part of the digestive tract. It absorbs water and stores food waste. The colon is about 5 feet long. The last part of the colon is the rectum. It's about 5 inches long.
How food moves through the colon
Semiliquid food waste from the small intestine enters the colon at the beginning of the colon (cecum). As this waste, called stool, travels through the colon, it loses water and solidifies. Strong muscles keep the stool moving through the colon. The stool is moved toward the last section of the colon (sigmoid colon). From there, it passes into the rectum, where it's stored until it leaves the body through the anus during a bowel movement.