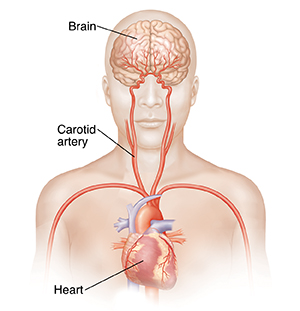
The brain needs a constant supply of blood to work well During a stroke, blood stops flowing to part of the brain. The affected area is damaged. Its functions are harmed or even lost. Most strokes are caused by a blockage in a blood vessel that supplies the brain (ischemic stroke). They can also occur if a blood vessel in the brain breaks open (ruptures). This is a hemorrhagic stroke.
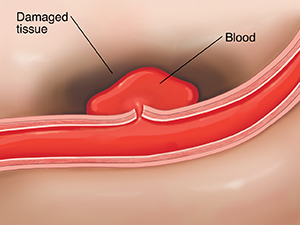
How a hemorrhagic stroke occurs
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures. This lets blood spill into or build up in nearby brain tissue. The extra blood presses on those brain cells. It can damage them or even cause them to die. Other brain cells die because their normal blood supply is cut off because of high pressure in the skull.